Securely Connect Remote IoT: Free P2P SSH Guide For Raspberry Pi
Are you struggling to manage your Internet of Things (IoT) devices securely and efficiently from anywhere in the world? The ability to establish secure connections to remote IoT devices using a peer-to-peer (P2P) SSH connection, especially on a Raspberry Pi, is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today's digital landscape. This is particularly true given the rise of the IoT and the increasing number of connected devices in our homes and businesses.
The evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) has opened up a world of possibilities, from smart homes and automated factories to sophisticated environmental monitoring systems. However, this explosion of connected devices has also created new security challenges. Data breaches, unauthorized access, and compromised systems are just a few of the risks that businesses and individuals face. Securing these devices, often deployed in remote or difficult-to-access locations, requires a robust and reliable solution. One that can be implemented affordably, without compromising on security.
This article will serve as a guide to navigate the complexities of establishing secure connections for your IoT devices, specifically focusing on using a free and effective method: Secure Shell (SSH) tunneling over a Peer-to-Peer (P2P) connection on a Raspberry Pi. The focus is on leveraging open-source tools and established security protocols to protect your data and maintain control over your devices. While the guide is targeted towards Raspberry Pi users, the underlying principles apply to a wide range of IoT devices.
- Try Undress Ai Free Today Remove Clothes With Ai
- Movie News Reviews Bollywood Tollywood More Find On Justwatch
Before diving into technical details, it's helpful to understand the core concepts and benefits of this approach. First, we will explore the fundamentals of SSH and P2P networking. Second, we will cover a practical implementation using a Raspberry Pi and then examine best practices for secure configuration, troubleshooting, and future trends in IoT technology.
Understanding the Benefits of P2P SSH
Securing remote IoT devices with P2P SSH offers several advantages. This method allows you to connect to your devices securely, even behind firewalls or on networks with restricted access. Unlike traditional methods that rely on complex network configurations or VPNs, P2P SSH creates a direct, encrypted tunnel between your local machine and the remote IoT device. All network traffic, including data and commands, is encrypted, preventing unauthorized access and data interception. With the right setup, you can access your Raspberry Pi remotely, monitor sensors, control actuators, and manage system settings from any location.
- Movierulz 2025 Latest Telugu Movies Trends Stay Updated
- Telugu Movies Movierulz Updates Latest News Streaming Info
SSH: The Foundation of Secure Communication
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure data communication between two networked computers. SSH provides a secure channel over an unsecured network by employing strong encryption. It allows you to remotely connect to and manage another device, like your Raspberry Pi, execute commands, transfer files, and tunnel other network connections. The robust encryption provided by SSH ensures that any data exchanged between the devices is protected from eavesdropping. SSH uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods to protect your data.
SSH uses a client-server model. A SSH client, running on your local machine, initiates a connection to the SSH server running on your remote IoT device (e.g., a Raspberry Pi). Once the connection is established, the client and server negotiate an encrypted channel. The server authenticates the client, typically using a username and password or SSH keys. Once the authentication is successful, the client can interact with the server as if it were directly connected to the device.
P2P: Bypassing Network Restrictions
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networking, in the context of IoT, allows devices to communicate directly with each other without needing a central server. This is particularly useful when devices are behind firewalls or on networks that restrict inbound connections. By establishing a P2P connection, you can create a secure, direct link between your local machine and your Raspberry Pi, bypassing these network restrictions. This means you can access your device from anywhere in the world, as long as both your local machine and your Raspberry Pi have an internet connection.
Setting up a Secure Remote IoT P2P SSH Connection: Step-by-Step Guide
Establishing a secure P2P SSH connection involves several key steps, from installing and configuring SSH clients and servers to testing the connection and implementing best practices for security. The following is a detailed guide to the process.
1. Prerequisites: Preparing your Environment
Before you begin, you'll need the following:
- A Raspberry Pi with an internet connection.
- A computer (local machine) with an internet connection.
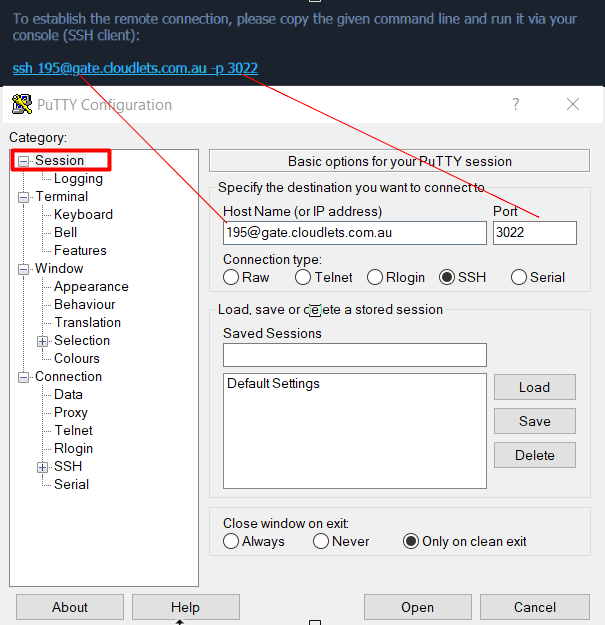
- An SSH client (e.g., OpenSSH, PuTTY) installed on your local machine.
- Basic knowledge of the command line interface (CLI).
- A user account with administrative privileges on your Raspberry Pi.
2. Installing and Configuring the SSH Server on Your Raspberry Pi
The Raspberry Pi typically comes with SSH already installed. However, to ensure it's properly set up and secure, follow these steps:
- Update your system: Open a terminal on your Raspberry Pi and run the following commands to update the package list and upgrade existing packages:
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgrade - Enable SSH: If SSH isn't already enabled, enable it using the Raspberry Pi configuration tool:
sudo raspi-configSelect "Interfacing Options" then "SSH" and enable it.
- Configure SSH Security: Configure the SSH server for improved security.
- Change the default SSH port: The default SSH port is 22, which is often targeted by attackers. Change it to a different, less common port. Edit the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config - Locate the line that begins with "Port 22" and change it to a new port number (e.g., "Port 2222"). Save and close the file (Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter).
- Disable password authentication: To further enhance security, disable password-based authentication and use SSH keys instead. In the `sshd_config` file, find the line that begins with "PasswordAuthentication" and change it to "no".
- Restart the SSH service: After making changes to the configuration, restart the SSH service to apply them:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
- Change the default SSH port: The default SSH port is 22, which is often targeted by attackers. Change it to a different, less common port. Edit the SSH configuration file:
3. Generating and Managing SSH Keys (Essential for Security)
SSH keys provide a more secure method of authentication than passwords. They use a pair of keys: a private key (kept secret on your local machine) and a public key (placed on the remote device). Here's how to generate and use SSH keys:
- Generate an SSH key pair on your local machine:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096Follow the prompts. You can choose a passphrase for additional security. This command generates two files: `id_rsa` (private key) and `id_rsa.pub` (public key).
- Copy the public key to your Raspberry Pi: Use the `ssh-copy-id` command to copy your public key to the authorized keys file on your Raspberry Pi. Replace `username` with your Raspberry Pi username and `raspberrypi.local` with the hostname or IP address of your Raspberry Pi:
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub username@raspberrypi.localIf you are using a custom SSH port use this command:
ssh-copy-id -p 2222 -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub username@raspberrypi.local - Test the key-based authentication: Try to SSH into your Raspberry Pi using your private key. You should be able to log in without entering a password.
ssh username@raspberrypi.localIf you are using a custom SSH port use this command:
ssh -p 2222 username@raspberrypi.local
4. Configuring P2P Tunneling (Using Tools like `autossh`)
To establish a P2P connection that persists even if the connection is interrupted, you can use a tool like `autossh`. `Autossh` is a program that automatically restarts SSH sessions and tunnels when they die. This ensures a reliable and continuous connection.
- Install `autossh` on your Raspberry Pi:
sudo apt install autossh - Create a reverse SSH tunnel from the Raspberry Pi to your local machine: Use the following command on the Raspberry Pi. This example assumes your local machine's IP is `192.168.1.100` and you want to access port 80 on the Raspberry Pi from your local machine. This creates a tunnel from port 8080 on your local machine to port 80 on the Raspberry Pi:
autossh -M 20000 -R 8080:localhost:80 username@your_local_machine_ip_address -p 2222
5. Testing the Connection and Accessing Your Raspberry Pi
After setting up the SSH server, generating keys, and establishing the tunnel, it's crucial to test your connection.
- Testing SSH Connection: From your local machine, try connecting to your Raspberry Pi using SSH. Use the following command, replacing `username` with your Raspberry Pi username and `raspberrypi.local` with the IP address or hostname of the Pi, and include the correct port number if you changed it:
ssh -p 2222 username@raspberrypi.localIf you're using SSH keys, you should be able to log in without entering a password. If you're using a custom port (e.g., 2222), make sure to include the `-p` flag followed by the port number.
- Verifying Port Forwarding: Once connected, try accessing a service running on your Raspberry Pi from your local machine. If you've set up port forwarding, for example, to access a web server on port 80, open a web browser and navigate to `localhost:8080`. If the forwarding is successful, you should see the web page served by your Raspberry Pi.
If you're still facing issues, review your configurations, check network connectivity, and consult the troubleshooting steps outlined below.
6. Best Practices for Secure Remote IoT Connections
Following best practices ensures the long-term security and reliability of your remote IoT connections.
- Regularly Update Your Software: Keep your Raspberry Pi's operating system and all installed software up to date with the latest security patches. Update the system by running the following commands periodically:
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgradesudo apt dist-upgrade - Use Strong Passwords and SSH Keys: Always use strong, unique passwords for all user accounts. However, consider using SSH keys as the primary authentication method, as they are more secure.
- Change Default Ports: Always change default SSH port (22) to a less common port to reduce the risk of automated attacks.
- Disable Password Authentication: After successfully setting up key-based authentication, disable password authentication in the SSH configuration file (`/etc/ssh/sshd_config`).
- Use a Firewall: Configure a firewall on your Raspberry Pi to control network traffic and block unauthorized access. This will help you filter traffic and set rules. The `ufw` (Uncomplicated Firewall) is a simple and user-friendly firewall for Linux systems.
sudo apt install ufwsudo ufw enablesudo ufw allow 2222 #Allow your custom SSH port.sudo ufw default deny incoming # Deny all incoming traffic by default - Monitor Your System: Regularly monitor your Raspberry Pi's logs (e.g., `/var/log/auth.log`, `/var/log/syslog`) for any suspicious activity. This can help you identify and respond to potential security threats.
- Limit Access: Only allow access to the necessary ports and services. Avoid exposing unnecessary services to the internet.
- Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Consider adding two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security, if supported by your SSH server.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Connection Refused: If you can't connect to your Raspberry Pi, check the following:
- SSH Service Status: Make sure the SSH service is running on your Raspberry Pi. Run: `sudo systemctl status sshd`.
- Firewall: Verify that your firewall isn't blocking SSH traffic.
- IP Address: Double-check that you are using the correct IP address or hostname of the Raspberry Pi.
- Port Number: Confirm that you are using the correct SSH port number (e.g., -p 2222).
- Authentication Problems: If you have issues with authentication:
- SSH Keys: Ensure that your SSH keys are correctly generated and copied to the authorized_keys file on your Raspberry Pi.
- Permissions: Verify that the permissions on your SSH key files and the .ssh directory are correct (e.g., the private key should be readable only by the user).
- Tunneling Issues: If the tunnel doesn't work:
- Port Forwarding: Check the port forwarding configuration. Verify that the ports are correctly mapped.
- Network Connectivity: Ensure that both your Raspberry Pi and your local machine have an active internet connection.
Future Trends in IoT Security
The landscape of IoT security is constantly evolving. Here are some future trends to keep an eye on:
- Zero-Trust Security: A zero-trust approach assumes that no user or device, inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. This model requires continuous verification and authorization before granting access to resources.
- AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to analyze network traffic and device behavior, identify anomalies, and proactively detect and respond to threats.
- Blockchain for Security and Trust: Blockchain technology can be used to secure IoT data, enhance device authentication, and ensure data integrity.
- Hardware-Based Security: More IoT devices are incorporating hardware-based security features, such as secure enclaves and trusted platform modules (TPMs), to protect sensitive data and code.
- Edge Computing Security: As edge computing becomes more prevalent, security at the edge of the network will become increasingly important.
Securely Connect Remote IoT P2P SSH Raspberry Pi: Free Download and Ultimate Guide
This comprehensive guide has outlined the steps to securely connect to remote IoT devices using a P2P SSH connection. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, the ability to establish secure connections to your devices is critical for protecting your data and enhancing your operations. This allows you to remotely access and manage your Raspberry Pi and other IoT devices from anywhere in the world. The methods can be implemented using free and open-source tools, making it accessible for anyone who wants to secure their IoT deployments without incurring costs.
Article Recommendations
- Movierulz 2025 Latest Telugu Movies Trends Stay Updated
- Trending Now Latest Telugu Releases More Refer Earn Gold


Detail Author:
- Name : Leanne Block IV
- Username : pschuster
- Email : astreich@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1987-06-23
- Address : 135 Schimmel Tunnel New Hayleymouth, WV 20862
- Phone : 872-810-3265
- Company : Hagenes LLC
- Job : Photographic Process Worker
- Bio : Hic cumque aut et error non et error sequi. Vitae eligendi aut optio in error.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/zella_xx
- username : zella_xx
- bio : Incidunt fugiat qui vero minus. In ut et consequuntur est. Ut ipsa sed illo odio. Similique sequi consequatur sed et dolores eius illum magni.
- followers : 4913
- following : 2829
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/zella500
- username : zella500
- bio : Mollitia dolores labore veniam et numquam. Laboriosam non non voluptatem ea.
- followers : 3322
- following : 1426
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/zmayer
- username : zmayer
- bio : Ut eum officiis et voluptas facere soluta. Officia rem dolores tempore.
- followers : 5261
- following : 79
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/zella5434
- username : zella5434
- bio : Blanditiis adipisci unde voluptas magni.
- followers : 285
- following : 2625
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@mayerz
- username : mayerz
- bio : Aut necessitatibus quam occaecati laborum incidunt illo.
- followers : 1596
- following : 59